According to a health survey, one in every three children in the UAE carry excess weight. 17 per cent of school children are obese and 66 per cent of adults carry excess weight. The UAE has an obesity rate that is double the world's average. These statistics are as alarming as the ill-effects of obesity itself.
It's not only a matter of looking physically fit or feeling attractive, obesity has a lot to do with the overall health status of people.
Rapid urbanisation, home delivery services and making food a central attraction of all celebrations have only added to the gravity of the situation. Read on to understand obesity, its complications and how to tackle it.
What is obesity?
According to the dictionary, the term 'obesity' translates to ‘the state of being grossly fat or overweight.’
In simple words, when you eat more than you burn, body fat starts to accumulate over a period of time, and if you fail to cut down the fat deposit, you soon become obese. Obesity is more than just an aesthetic concern, it is a complex disorder that can affect a person’s health and well-being, if left unchecked.
Body Mass Index is a popular tool used to measure obesity. Having a BMI greater than 30 is classified as obesity. BMI is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by his or her height in metres squared.
Dr Davide Mineo, Specialist in Endocrinology, Metabolic Diseases and Nutrition at MDM, Dubai said, "Obesity is generally classified by means of the BMI-body mass index that evidence from 19 up to 25 as the normal value, up to 29 as overweight, and from 30 and above as obesity (e.g. mild up to 35, moderate between 35 and 40, severe over 40)."
Another method to measure obesity is waist circumference, which is a less common method.
“Waist circumference can easily be measured by a tape measure around the area below your last ribs. A waist circumference of more than 88cm (34 inches) in women, or 102cm (40 inches) in men is considered unhealthy”, explains Dr Ilaria Saredi, Family Medicine Specialist at Allied Medical Center - Dubai.
Medical experts in Dubai have highlighted few lesser known facts about obesity
Dr Abdul Kader Weiss, General & Laparoscopic Surgeon at Emirates Speciality Hospital explains "the weight gain resulting from the increase in muscle mass does not fall within the concept of obesity as a term that refers to a medical problem that needs to be managed and treated."
Dr Carole Wehbe Chidiac, MD, Specialist Family Medicine at GMCClinics- "As per the World Health Organisation Obesity is not defined by a shape or weight, it is a state of excessive fat accumulation associated with negative medical consequences.
Main causes of obesity
Many people seem to believe that overeating and lack of willpower to hit gyms cause obesity. But, this might not be entirely true. There are a number of genetic and medical reasons as well behind it.
Here’s a quick glance over other causes:
Medical /Genetics factors as explained by Dr Khaled Koky, Consultant Internal Medicine at Burjeel Speciality
• Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)- PCOS causes an imbalance in a woman’s reproductive hormones, and one of its symptoms is weight gain.
• Prader-Willi syndrome- Is a condition that causes excessive hunger in those afflicted by it.
• Cushing syndrome- Cushing’s syndrome results in an increase in the cortisol levels in the body. And one of the major side effects of this condition is weight gain.
• Hypothyroidism- Another condition in which the dysfunction of the thyroid gland can lead to weight gain.
Lifestyle factors as explained by Dr Minu Sandeep, General Practitioner at Aster Clinic, Al Qusais 2
"Sedentary life styles, decreased structured physical activity, increase sugar containing food and drinks, fast food services, TV watching (especially eating while watching and in children), computer games, eating during the night, disturbed sleeping. Other reasons are pregnancy, smoking cessation, prolonged sickness that prevent mobility, viruses and toxins."
Health risks associated with obesity
Obesity goes beyond one’s weight and looks. Unhealthy weight gain places an extra pressure on a person’s organs, muscles and bones and might affect the way the body operates. Of all the health risks associated with obesity, the most prevalent ones are high cholesterol, type two diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, sleep apnea, cancer, infertility, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, arthritis and mental health conditions due to the effects of weight gain on aesthetics.
Dr Carole Wehbe Chidiac of GMCClinics has highlighted the possibility of obesity being linked to a negative quality of life. She explains, “people with obesity are often asked to lose weight for all their concerns without a proper diagnosis and any alternative management, at least until they lose the weight. This leaves them more frustrated and less equipped to lose the weight."
How to prevent obesity
Obesity prevention begins at a young age. Families are encouraged to build children’s strong relationship with healthy food. Some of the steps include limiting unhealthy food in the household, capping screen time, indulging in fun and exciting physical activity, eating healthy food as a family, eating slowly and only when hungry, and making sure that everyone is getting enough sleep.
To prevent obesity in adulthood, Alaa Takidin of Canadian Hospital suggests eating at least five servings of fruits and vegetables daily, cut down your consumption of fatty and sugary foods, use low fat or fat free dairy product rather than the full fat ones, control food portion sizes, choose whole grain foods such as brown rice and whole wheat bread, avoid highly processed foods made with refined white sugar, flour and saturated fat, increase water intake; at least 1.5 litres a day. "According to the American guidelines it is recommended to exercise four or five times per week, for 40-45 minutes per session, with aerobic activities such as brisk walking or equivalent," said Dr Kamal Akkach, Consultant in Internal Medicine, CEO and Founder of HealthBay.
Nutrition Director, Lauren Jacobsen at Kcal said, “Getting the right nutrition is critical. Eating less food is one way, but eating the right foods will also help with your success. A diet of primarily fresh, whole foods, void of processed foods, will provide the body with all the nutrients it needs to function. Aim to eat at regular times throughout the day to keep blood sugar levels balanced and avoid getting hungry. Fill up on a variety of vegetables including leafy greens, broccoli, and root vegetables such as sweet potato, along with some fibrous fruit such as berries and apples. Proteins should include poultry, whole eggs, lean red meat, fish or veggie protein sources such as beans and legumes. Lastly, consider adding healthy fats from nuts, seeds, avocado and healthy oils such as olive and coconut.”
Treatments for obesity
People who struggle with severe obesity have surgical and non-surgical options available to them, so they can lose weight depending on their circumstances and according to patient needs.
Medication
“There are many drugs that can be used to control weight in the case of a failure to modify life style. It is also recommended to not use medication until the BMI is more than 30”, said Dr. Khaled Koky of Burjeel Speciality.
Bariatric Surgery
“Bariatric surgery should be reserved for those whose BMI is more than 40 and who did not met the weight loss goals with diet, exercise, and drug therapy. Many procedures can be done after evaluating the patient condition”, adds Dr Khaled Koky.
“Among the morbidly obese, less than five percent succeed in losing a significant amount of weight and maintaining the weight loss with non-surgical programs, so surgery is often the most effective treatment”, said Dr Hussam Al Trabulsi, Specialist General and Bariatric surgeon at Medcare Hospital.
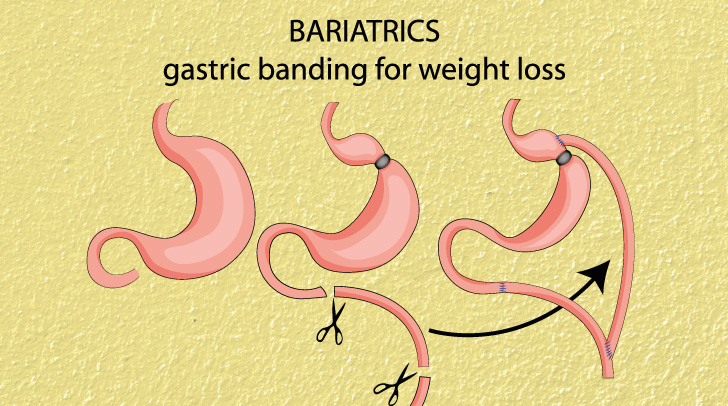
Surgical options include the laparoscopic gastric bypass in which the surgery causes patients to feel full after eating a small amount of food. There are also gastric bands or sleeves, which are placed around the stomach and limit
food intake.
Prevention is better than cure and with obesity becoming an increasingly serious problem, impacting multiple areas of personal health, it is important that we get proactive. The onus is on us to implement these changes at home by embracing a healthy balanced lifestyle.